A single drive failure will rebuild. The various types of RAID levels are as follows.

Raid Level 0 1 5 6 And 10 Advantage Disadvantage Use
Larger size and higher speed than RAID-1 and more redundancy than RAID-0.
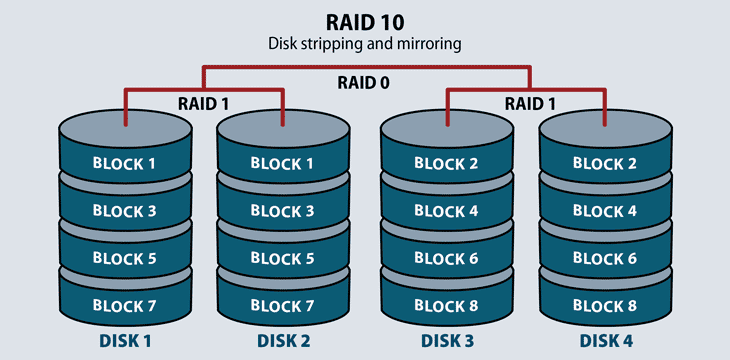
. If a drive fails the controller uses either the data drive or the mirror drive for data recovery and continues operation. Standard nested and nonstandard RAID levels. Selecting the suitable raid level for your application depends on the following things.
Good performance no striping. Standard nonstandard and nested. Good redundancy distributed.
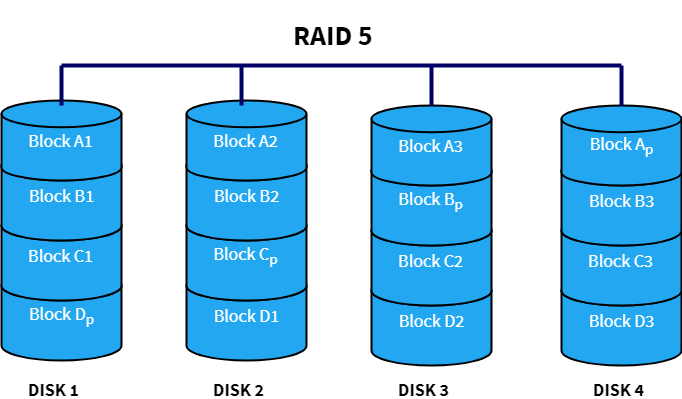
If goes fairly deeply into the theory and implementation but diagrams are provided to help. There are six basic RAID levels. RAID level 5 distributes the parity block and data on all disks.
Standard RAID levels. Raid level based on the level of redundancy it provides. RAID-6 is a recent advancement that contains a distributed double parity which involves block-level stripping with 2 parity bits instead of just 1 distributed across all the.
It uses the mirroring technique. This level doesnt provide fault tolerance but increases the system performance. RAID Level 0 stripes data across two or more drives.
Additionally you can choose how to implement RAID on your system. This numbered system enabled those in IT to differentiate RAID versions. RAID-2 consists of bit-level stripping using a Hamming Code parity.
RAID levels explained. A nonstandard RAID level is set to the standards of a particular company or open source project. The number of levels has been broken into three categories standard nested and non-standard RAID levels.
What Are the Different RAID Levels. These two are less commonly used. Four or more drives are made into two mirrors that are striped.
Software RAID is part of the OS and is the easiest and most cost effective implementation. It utilizes full storage capacity. RAID LEVEL 1.
It is based on stripping that means if one disk fails then all data in the array is lost. The total array size is reduced by parity. This level can survive multiple simultaneous drive failures.
The reliability and performance implications of the various RAID levels will be discussed in detail here. RAID level 0 provides data stripping ie a data can place across multiple disks. Standard levels of RAID are made up of the basic types of RAID numbered 0 through 6.
RAID 0 Disk striping. Therefore you can choose between hardware RAID software RAID and firmware RAID. 0 1 4 5 6 and 10 10.
RAID-3 consists of byte-level striping with dedicated parity. RAID levels can be broken into three categories. What about the other RAID levels.
RAID Redundant Array of Independent Disks is a technology to improve disk performance and data storage reliability. There is no arrangement in case data is lost. It also evolves several levels like RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 2 RAID 5 etc.
It has striping but no redundancy of data and offers the best performance but no fault-tolerance. Different types of RAID levels. Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 5.
RAID 0 splits data across any number of disks allowing higher data throughput. Excellent redundancy as blocks are mirrored. You can select a raid level based on the performance that it provides.
RAID 0 gives good readwrite performance but doesnt provide data redundancy. It does not require the use of an additional often costly piece of hardware and the proprietary firmware. Each RAID level is offering a trade-off of data protection system performance and storage space.
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 1. The original paper that coined the term and developed the RAID setup concept defined six levels of RAID -- 0 through 5. The following list explains the standard RAID levels 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 and popular non-standard and hybrid options RAID 10.
Standard RAID levels RAID 0. RAID level 4 is similar as RAID level 3 but it has Block-Interleaved parity instead of bit parityYou can access the data independently so read performance is high. RAID 0 - based on striping technique.
This can be used in organizations where high performance and security are required. Pg No137 8 ii Illustrate indexing and hashing techniques with suitable examples8 Pg No142 Or b Write short notes on 88 Spatial and multimedia databasesPg No153 Mobile and web databasesPg No156 a i Describe the GRANT functions and explain how it. Here is a list of the most used RAID levels.
List the different levels in RAID technology and explain its features. RAID 1 - utilizes mirroring technique increases read speed in some cases and provides fault tolerance in the loss of no more than one member disk. Good performance as blocks are striped.
Lets discuss some of the widely used raid levels. This type is also known as disk mirroring and consists of more than two drives that duplicate the storage of. The number of levels has since expanded and has been broken into three categories.
The RAID is mainly divided into hardware RAID and software RAID. Data is simply striped across multiple disks for parallel storage and retrieval. Below are the following most popular and standard RAID levels.
RAID 10 RAID 10 This level performs Mirroring of data prior stripping which makes it much more efficient and redundant as compared to RAID 01. Data are stored twice by writing them to both the data drive and set of data drives and a mirror drive or set of drives. Five of RAID levels are commonly used they are.
RAID 0 or No RAID. Many different ways of distributing data have been standardized into various RAID levels. This RAID level doesnt provide fault tolerance but increases the system performance high read and write speed.
This paper will try to explain the different RAID levels along with their individual strengths and weaknesses. Striped set of Mirrored Subset. They each have their pros and cons regarding the balance of speed and security.
There are 6 different levels or volume types of RAID. Raid level based on read and write operations. 9 rows Large size fast speed and redundancy.

Raid Levels Explained Enterprise Storage Forum
0 Comments